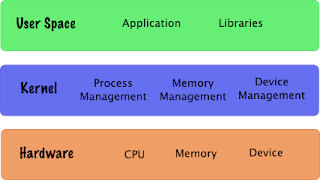
Que:- Define the Operating System.
Ans:- An operating system is a group of program that manages co-ordinates and controls the actions of the computer hardware and software.
Que:- What is the function of an Operating System.
Ans:- An OS proceed as an interface between the user and the computer. It act as the manager of the property of the computer.
Que:- Write the functions of an Operating System.
Ans:-
- Memory Management.
- Processor management.
- Interrupt Handling.
- Accounting.
- Automatic job sequencing.
- Management and control of I/O devices
Que:- What is the necessitate for an Operating System?
Ans:- A medium is desired to communicate between the user and the H/W. An OS acts as a medium of interface.
Que:- What are the characteristics of an OS.
Ans:-
- User affable.
- Preserve track of the status of EACH RESOURCE.
- Allows share of resources (H/W and S/W).
- Provides adequate security.
- Security.
Que:- What is a process?
Ans:- A process is mainly a program in execution. It is the component of work in a present operating system.
Que:- What is meant by a process state?
Ans:- When a process carries out, it changes, its position, this is recognized as process state.
Que:- What are the different process states?
Ans:- The diverse process states are:-
- New
- Ready
- Running
- Waiting
- Terminated
Que:- How does a process fluctuate from a job?
Ans:- A process is an active body with a program counter identifying the next instructions to perform and a set to associated resources, whereas a batch system executes jobs. (This is a collection of processes).
Que:- Differentiate program and a process?
Ans:- A process is a program in implementation. A program is a passive unit,
Where as a process is an active unit.
Que:- What is Process Control Block?
Ans:- Every process is represented in the operating system by a process control Block (PCB) also called a task control block.
Que:- What is the function of a Process Control Block?
Ans:- A Process Control Block (PCB) encloses several pieces of information related with a specific process. It serves as the warehouse for any information that may vary from process to process.
Que:- What is the information restricted in a PCB?
Ans:- A PCB contains section of information related with a specific process, namely:-
- Process state
- Program counter
- CPU register
- CPU scheduling information
- Memory management information
- Accounting information
- I/O status information
Que:- What are the operations on process?
Ans:-
- Create a process
- Destroy a process
- Defer a process
- Resume a process
- Change the priority of a process
- Block a process
- Stir a process
- Transmit a process
- Enable a process to communicate with another
Que:- What are the operations concerned in creating a process?
Ans:-
- Name the process.
- Insert it in the system’s known processes list (or) process table.
- Establish the process’s initial precedence.
- Produce the process control block.
- Allocate the process’s initial resource.
Que:- What is the kernel of an operating system?
Ans:- Kernel is the ingredient of the OS which directly creates interface with the hardware system.
Que:- What are the main functions of the kernel?
Ans:- To make available mechanism for:-
- Formation and erasure of processes.
- Inter process communication.
- Management of processes.
Que:- What are the components of an Operating System?
Ans:- Operating System which is a set of programs is of 2 types:-
- Control program.
- Supervisory program.
Que:- What is multi programming?
Ans:- The facility of observance several jobs in the memory at one time, where the CPU is switched back and forth along with them are known as Multi programming.
Que:- What is the use of Multi Programming?
Ans:- Multi programming helps to augment CPU consumption, and to reduce the total time required to execute the jobs.
Que:- Demonstrate the factors that generally conclude the degree of Multi Programming.
Ans:-
- The number of Programs exists in Primary memory.
- Passing of the control of the CPU hurriedly among these programs.
- Security of user process from one another.
Que:- What is the remuneration of Multi Programming?
Ans:-
- Look up the System Performance.
- Consent to Time Sharing.
- Supports many instantaneous interactive users.
Que:- Clarify, what is Multi Processing?
Ans:- Multiprocessing is utilized of two or more central processing units inside a single computer system. The phrase also refers to the capacity of a system to sustain more than one processor and/or the capacity to distribute tasks among them.
Que:- What is the benefit of Multi Processing Systems?
Ans:- A Multi Processing System is one in which there are additional than one CPU, interleaved with each other. Thus it assists in improving the capacity of work done.
Que:- What are the categories of Multi Processing?
Ans:-
- Symmetric Multi Processing.
- Asymmetric Multi Processing.
Que:- What is Symmetric Multi Processing?
Ans:- It is one in which each processor runs a one and the same copy of the operating system and these copies correspond with one another as required.
Que:- What is Asymmetric Multi Processing?
Ans:- It is one in which each processor is allocated a precise task. A Master Processor controls the system and the other Processors are owed job by the Master Processor.
Que:- What is Time Sharing?
Ans:- Time Sharing (Multi tasking) is a consistent extension of Multi Programming. It is a form of Multi Programmed OS which operates in an interactive mode with rapid reaction time.
Que:- Clarify the concept of Time Sharing?
Ans:- Multiple Jobs are performed by the CPU switching between them, but the switches happen so repeatedly that the users may interrelate with each program even as it is running.
Que:- What is the advantage of Time Sharing?
Ans:- A Time Sharing system allocates many users to concurrently allocate the computer resources.
Que:- Describe the Real Time System.
Ans:- It is another form of operating system which is used in environments where a large number of events frequently external to the computer system must be conventional and processed in a short time or within convinced deadlines.
Que:- Give some examples of Real Time Application.
Ans:- Examples are:-
- Flight Control.
- Real Time Simulation.
- Military Application.
- Petroleum Refinery.
- Process Control etc.
Que:- What is On-Line Processing?
Ans:- Transferring the contents from the input directly on to the CPU and relocate the processed contents onto the printer is On-Line Processing.
Que:- Explain Off-Line Processing?
Ans:- Rather than the CPU reading directly from the input, copying the content into CPU and PROCESS.
For Information About DBMS Guide Check:- http://dbmsbook.blogspot.com
For Information About Spectroscopy Book Check:- http://spectroscopybook.blogspot.com/
For Information About Operating System (OS) Book Check:- http://operatingsystembook.blogspot.com
Check Labels For more Similar Posts:-